OverviewUse the Building Data screen to enter the following for each section of the estimate: Stories in Section and in Building |
Related Topics |
Use this line to do the following:
Select a Section: Select the section to view or edit, which displays its Building Data, using the Select Section drop-down list:
![]()
Add a Section: Click the New button.
Delete a Section: Click the Delete button.
Add a Basement: To add a basement, click the Basement button. This button is only visible if the estimate does not have a basement.
Move From Section to Section: Use the ![]() buttons to move to the Previous or Next sections respectively.
buttons to move to the Previous or Next sections respectively.
Note: When you delete a section, Commercial Estimator does not automatically renumber the remaining sections. For example, suppose you have the following three sections:
Section 1
Section 2
Section 3
If you delete Section 2, you will have the following sections:
Section 1
Section 3
You should change "Section 3" to "Section 2" If you do not do this and thhen add another section, you will have the following sections:
Section 1
Section 3
Section 3
The section title prints at the top of each section in the report to identify the section. Commercial Estimator automatically sets the section titles to "Section 1," "Section 2," etc. You can optionally change the Section Title to better identify section by typing a different section title in this field.
Example: If Section 1 is the original portion of the building and Section 2 is an addition made to the building in 1995, you could change the section titles as follows:
|
Section 1 |
Original Building |
|
Section 2 |
1995 Addition |
The total floor area of a section is the total area on all floors based on the building's exterior dimensions. When calculating total floor area, do not include any of the following: Basements, mezzanines, balconies, unfinished attics, exterior porches, decks, patios or garages.
When entering total floor area, do not include commas. Total area is required—you must enter it in each section of the estimate.
Commercial Estimator has two fields for number of stories: the number of stories in the section of the building, and the total number of stories in the building. In many cases, these values will be the same. In such cases, you only need to enter the number of stories in the section—Commercial Estimator will automatically set the number of stories in the building to this value.
Estimate with One Section: If your estimate has only one section, enter its number of stories in "Number of Stories: Section" only.
Vertically Sectioned Building: If you vertically section a building, enter the number of stories in each section under "Number of Stories: Section."
Example: A building that is part 6 stories and part 3 stories can be vertically sectioned as follows:
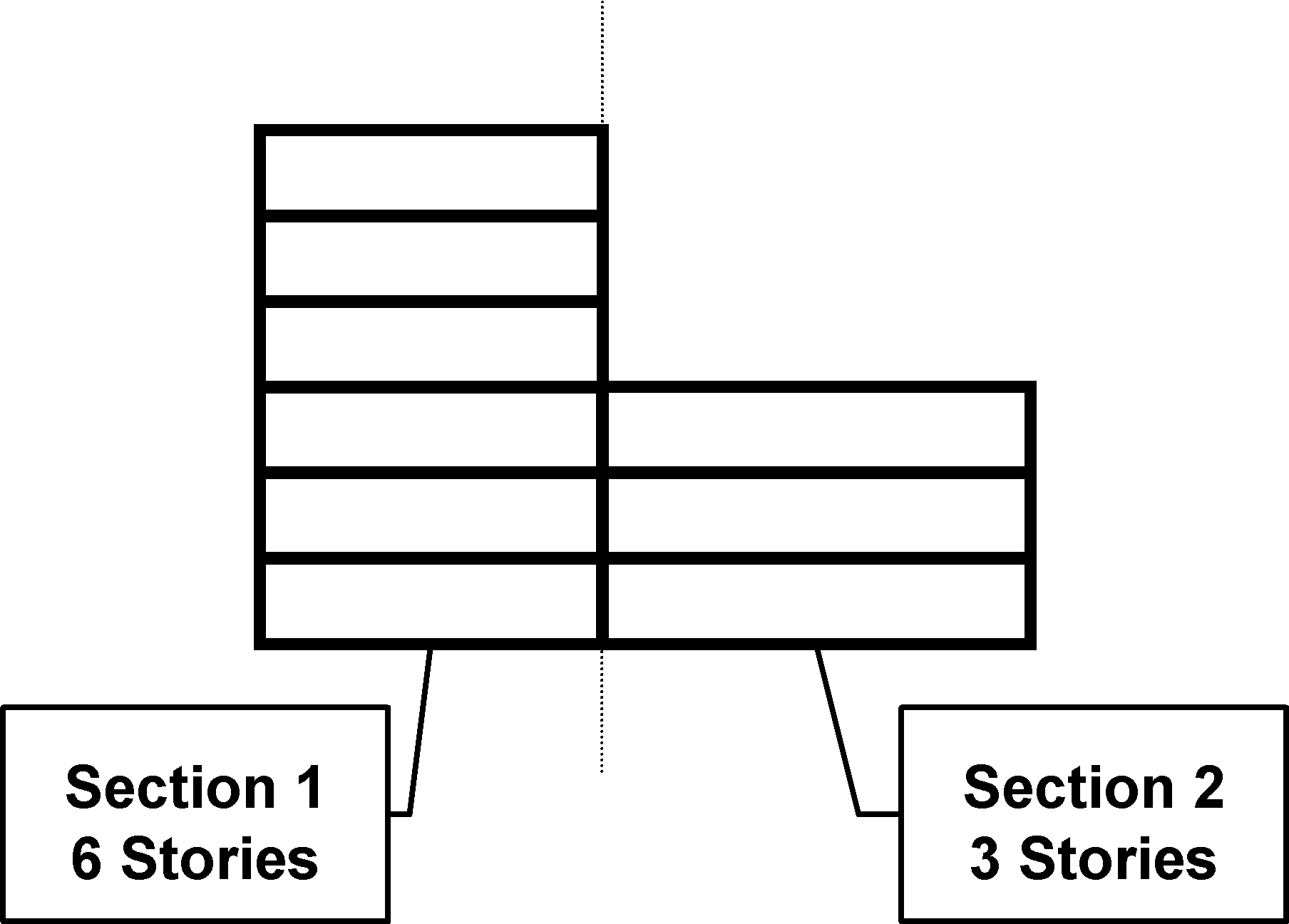
Horizontally Section Buildings: If you horizontally section a building, enter the number of stories in each section under "Number of Stories: Section," and the total number of stories in the building under "Number of Stories: Building."
Example: A building that has a one-story bank on the first floor (20' story height), and five stories of offices on the second through sixth stories (10' story height), is sectioned horizontally as follows:
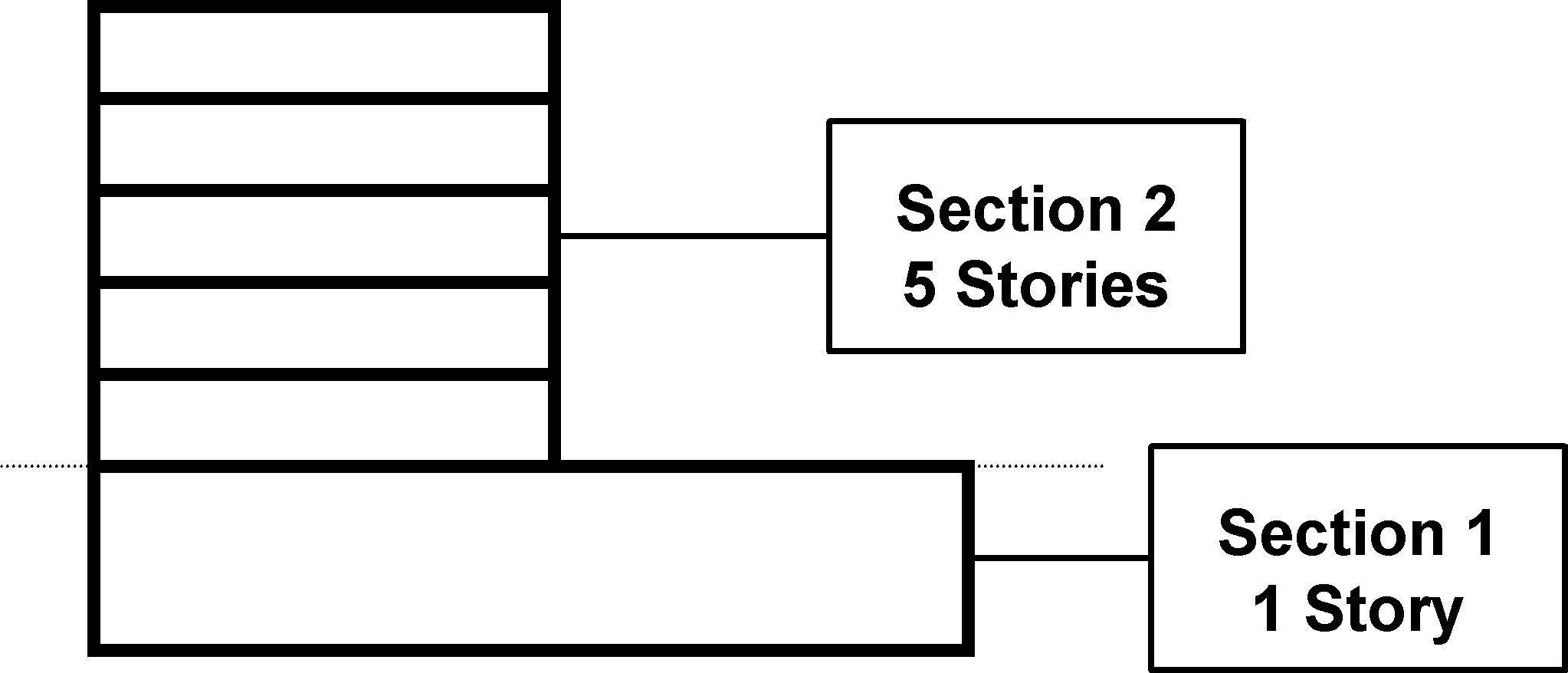
For a multistory building, Commercial Estimator uses the number of stories to adjust the costs for high-rise construction (by taking into consideration the additional framing required in multi-level buildings as well as the cost of raising material and labor to the upper floors).
You must enter either the shape or the perimeter for the building:
Shape: Select one of the following shapes, which Commercial Estimator uses to automatically calculate the perimeter:
Square
Rectangular (or Slightly Irregular)
Irregular
Very Irregular
If you select any of these shape options, the word "Calculated" displays for the perimeter. This indicates that Commercial Estimator will automatically calculate the perimeter based on the shape (together with the total floor area and the number of stories).
Perimeter: To enter the perimeter directly, select the following:
Manual Perimeter
The perimeter is the total linear feet of wall that encloses the floor area on a single floor (based on exterior dimensions). If the perimeter varies in a multilevel basement, enter the average perimeter.
Example: If a 10-story building has a perimeter of 660 feet on the first floor and 500 feet on the other 9 floors, the average perimeter is (660 times 1) + (500 times 9), all divided by 10, or 516 feet.
If you horizontally section this building with the first floor in section 1 and the other nine floors in section 2, the entries are:
|
Section 1: |
Stories in Section: 1 |
|
|
Stories in Building: 10 |
|
|
Perimeter: 660 |
|
Section 2: |
Stories in Section: 9 |
|
|
Stories in Building: 10 |
|
|
Perimeter: 516 |
Important: It is best to enter the perimeter if you know it.
Note: For shed buildings that typically have one open side (i.e., no wall on one side), you should enter the perimeter as the number of linear feet of the sides of the shed with walls (i.e., do not include the side with no wall). If you enter a shape for shed buildings, Commercial Estimator calculates the perimeter assuming only three walls. Given this, when entering wall components for such buildings, the wall percentages should total 100%.
The effective age of a building is its age in years as compared with other buildings performing like functions. It is the actual age less any years that have been taken off by face-lifting, structural reconstruction, removal of functional inadequacies, etc.
Use the following steps to determine the effective age of a building:
Typical Life: Determine the building's typical life, based on its occupancy and quality, using the "Typical Lives" table contained in the occupancy's help.
Remaining Useful Life: Estimate the building's remaining useful life, based on an evaluation its condition, construction quality, actual age and any renovations or repairs that have been made.
Effective Age: Subtract the remaining useful life from the typical building life to obtain the effective age.
Example: For a good quality, Class C office building built 30 years ago, the following renovations and repairs have been completed:
The electrical system was replaced 10 years ago.
The heating plant was replaced 4 years ago.
The roof was repaired 8 years ago.
The interior was completely renovated 10 years ago, with new floor covering, wall finish and plumbing fixtures.
Based on the office building's current condition and a subjective evaluation of the effect of these changes, you estimate that the remaining useful life is now 45 years. The Typical Lives table in the help for occupancy 344 (Office Building) is:
|
|
|
|
|
|
Class |
|
|
|
|
|
Quality |
A |
B |
C |
D |
H |
M |
P |
S |
W |
|
Low |
50 |
50 |
45 |
40 |
-- |
-- |
40 |
40 |
-- |
|
Average |
55 |
55 |
50 |
45 |
-- |
-- |
45 |
45 |
-- |
|
Good |
60 |
60 |
55 |
50 |
-- |
-- |
50 |
50 |
-- |
|
Excellent |
60 |
60 |
55 |
50 |
-- |
-- |
50 |
50 |
-- |
From this table, the typical life is 55 years. Therefore, the effective age is:
|
Typical Building Life |
55 years |
|
Minus: Remaining Useful Life |
-45 years |
|
Effective Age |
10 years |
The entry of Effective Age is optional. When you enter it, Commercial Estimator automatically calculates the amount of normal physical and functional depreciation. This calculation uses the depreciation schedule in the Marshall Valuation Service, based on the occupancy, class and quality in addition to effective age. You can override the automatic calculation by making an entry for combined physical & functional depreciation, or for physical and/or functional depreciation separately.
Commercial Estimator automatically computes the normal physical and functional depreciation based on the occupancy, class, quality and effective age. This calculation does not include either abnormal or excessive functional depreciation, or any external obsolescence, which you must add separately.
You can override this automatic calculation by making an entry for either combined physical & functional depreciation, or for physical and/or functional depreciation separately.
This is the combined percentage for normal physical and functional depreciation to be subtracted from the replacement cost new when computing the depreciated cost. This prints in the report as a single line, “Physical and Functional Depreciation.” This overrides the automatic calculation based on occupancy, class, quality and effective age.
Example: If you enter 12.5% for combined physical and functional depreciation, the report includes the following:
Units Cost Total
Replacement Cost New 20,000 68.53 1,370,600
Less Depreciation
Physical & Functional 12.5% 171,325
Depreciated Cost 20,000 59.96 1,199,275
These fields set separate values for physical and functional depreciation, which are printed as separate lines in the report. Entering either of these overrides the automatic depreciation calculation based on occupancy, class, rank and effective age.
Example: If you enter 12% for physical depreciation and 7.5% for functional depreciation, the report includes the following:
Units Cost Total
Replacement Cost New 20,000 68.53 1,370,600
Less Depreciation
Physical 12.0% 164,472
Functional 7.5% 102,795
Depreciated Cost 20,000 55.17 1,103,333
Enter the percentage the external depreciation only to be subtracted from the replacement cost new when computing depreciated costs. Making an entry in this field has no effect on the automatic depreciation calculation.
Example: If you enter 12.5% for external depreciation, the report contains the following:
Units Cost Total
Replacement Cost New 20,000 68.53 1,370,600
Less Depreciation
External 12.5% 171,325
Depreciated Cost 20,000 59.96 1,199,275